Stone Surgeries
Stone surgeries, also known as lithotripsy or urological stone procedures, are medical interventions performed to treat various types of stones that can form in the body. The most common types of stones are kidney stones, bladder stones, and gallstones, but stones can also form in other organs and ducts. Stone surgeries are typically performed by urologists, general surgeons, or other specialists, depending on the location of the stones.
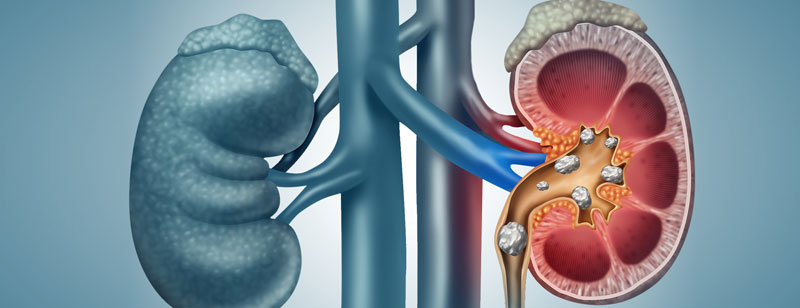
Renal Stone
Renal stone management often involves the use of various surgical procedures, depending on the size, location, and composition of the kidney stones. Two common surgical techniques used for renal stones are Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) and Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS):
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL):
- Procedure: PCNL is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove or break down large kidney stones that cannot be managed through less invasive techniques.
- Process: A small incision is made in the patient's back, and a narrow tube (nephrostomy tube) is inserted through this incision to access the kidney. A nephroscope is then passed through the tube to visualize the stone. The stone can be broken down using specialized instruments, like lasers or ultrasonic probes, and the fragments are then removed or allowed to pass naturally.
Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS):
- Procedure: RIRS is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure used to treat kidney stones, particularly those located in the renal pelvis and upper ureter.
- Process: A flexible ureteroscope is passed through the urinary tract into the kidney. The surgeon can then visualize the stone and use laser or other energy sources to fragment it. The broken-down stone fragments can be removed or passed naturally through urine.
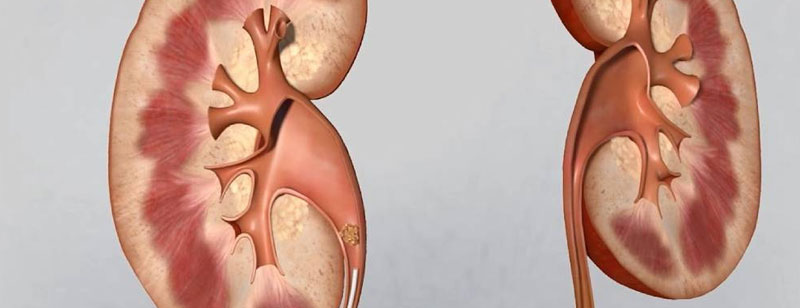
Ureter Stone
Ureteral stones can be treated using a minimally invasive surgical technique known as Ureteroscopy (URS) or Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS), as previously mentioned in the context of kidney stones. URS and RIRS are both commonly used to address stones in the ureter. Here's more information on URS:
Ureteroscopy (URS):
- Procedure: URS is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure used to diagnose and treat ureteral stones. It involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube called a ureteroscope into the ureter, allowing the surgeon to directly visualize and manipulate the stone.
- Process: After the ureteroscope is passed through the urinary tract and into the ureter, the stone is located and then broken into smaller fragments using laser or other energy sources. These smaller stone fragments can be removed or allowed to pass naturally through urine.
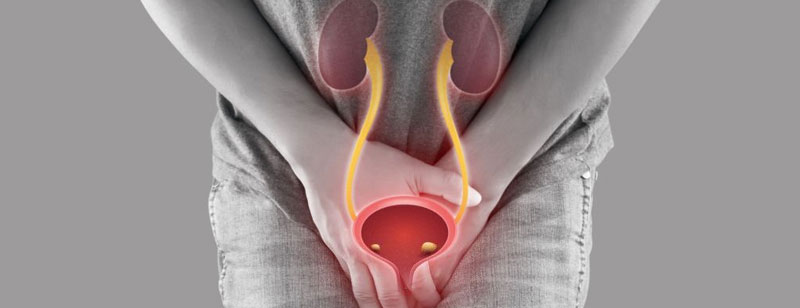
Bladder Stone
Bladder stones are solid masses that form in the bladder and may need to be removed through various surgical procedures, depending on their size and composition. Three common surgical techniques used for the treatment of bladder stones are Percutaneous Cystolithotripsy (PCCL), Cystolithotripsy, and Suprapubic Cystolithotripsy (SPCL):
Percutaneous Cystolithotripsy (PCCL):
- Procedure: PCCL is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove bladder stones. It involves making a small incision in the lower abdomen and inserting a tube (cystoscope) through the abdominal wall and into the bladder. The stone is then broken into smaller fragments using a lithotripter (stone-breaking device), and the fragments are removed or flushed out.
Cystolithotripsy:
- Procedure: Cystolithotripsy is an endoscopic procedure performed using a cystoscope, a thin tube with a camera and specialized instruments. The cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder, and the stone is directly visualized. Energy sources like laser or ultrasound are used to break the stone into smaller pieces, which can then be removed or passed naturally through urine.
Suprapubic Cystolithotripsy (SPCL):
- It is used to treat larger stones not amendable to removal by endoscopic methods . A small pfanensteil incision is made suprapubically . Bladder is opened and stone is retrieved en masse