
Minimally invasive surgery minimizes patient recovery time , reduces post operative pain, early return to work, decreases chances of wound infection,etc
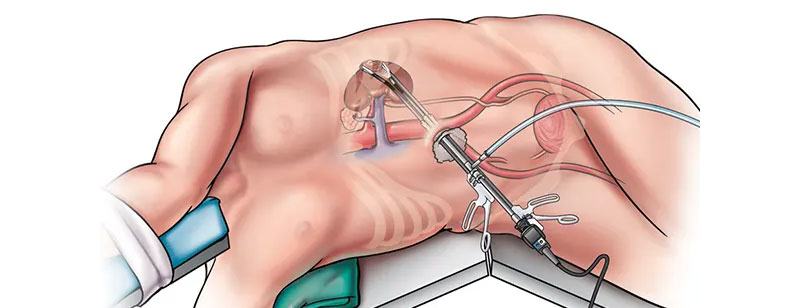
Laparoscopic nephrectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to remove one or both kidneys. It has become the preferred approach for many kidney surgeries due to its numerous advantages over traditional open surgery.
During a laparoscopic nephrectomy, a series of small incisions are made in the patient's abdomen, typically three to four in number. Through one of these incisions, a laparoscope, which is a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and light source, is inserted. This laparoscope provides the surgical team with a magnified, high-definition view of the surgical area on a monitor. Through the remaining incisions, specialized surgical instruments are introduced.
The surgeon then carefully detaches and removes the kidney, either partially or entirely, depending on the specific medical condition. Laparoscopic nephrectomy can be used for various reasons, including treating kidney cancer, addressing non-functioning or diseased kidneys, and providing kidneys for transplantation.
This minimally invasive technique offers several advantages, such as reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and minimal scarring. Patients often return to their normal activities more quickly than with open surgery. However, it is important to note that patient eligibility for laparoscopic nephrectomy is determined on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the individual's specific medical condition and overall health. As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, which should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Laparoscopic orchidopexy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat undescended testicles, a condition known as cryptorchidism, which commonly occurs in infants and young boys. During this procedure, a surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen to access and reposition the undescended testicle into the scrotum.
The surgeon employs a laparoscope, a thin tube equipped with a camera and specialized instruments, to guide the surgery. This allows for a magnified, high-definition view of the abdominal cavity on a monitor. The testicle is carefully located, freed from any attachments, and secured in the scrotum using stitches or a small mesh pouch to prevent future re-ascension.
Laparoscopic orchidopexy offers several benefits, including minimal scarring, reduced postoperative discomfort, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to open surgery. This minimally invasive technique is a safe and effective means of correcting undescended testicles in children and promoting normal testicular development and function.
Laparoscopic ureterolithotomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove kidney or ureteral stones that are causing blockages or pain. This technique is typically employed when other treatments, such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or ureteroscopy, have proven ineffective or unsuitable for the specific stone size or location.
During a laparoscopic ureterolithotomy:
Laparoscopic ureterolithotomy offers advantages such as minimal scarring, shorter hospital stays, reduced postoperative pain, and a faster return to normal activities. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, which should be discussed with a healthcare provider. This approach is particularly valuable for certain complex cases of urolithiasis and is chosen based on the stone's size, location, and the patient's individual circumstances.
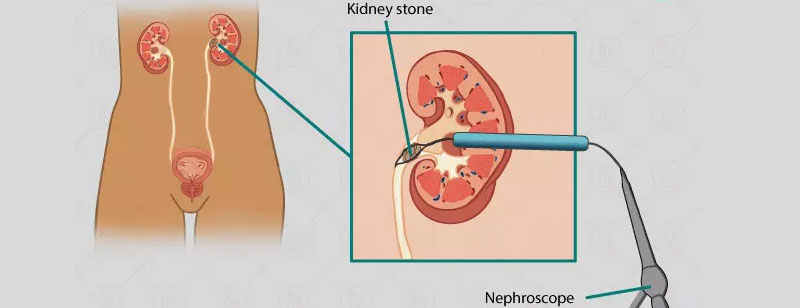
Laparoscopic-Assisted Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to remove large kidney stones or complex renal calculi. It combines the benefits of laparoscopy and percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the effective treatment of kidney stones that are difficult to manage with traditional approaches.
During the procedure:
Laparoscopic-assisted PCNL combines the advantages of both laparoscopy and PCNL, offering minimal scarring, reduced postoperative pain, and a faster recovery compared to open surgery. This approach is particularly suitable for patients with large, complex, or multiple kidney stones. However, as with any surgical procedure, potential risks and complications should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment for the patient's specific condition.
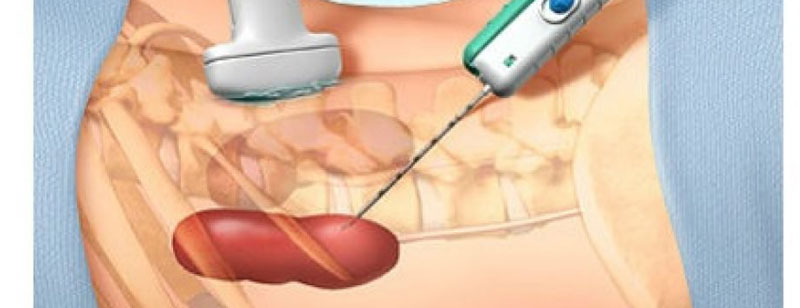
Laparoscopic cyst deroofing is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat various types of cysts, often within the abdominal or pelvic regions. This technique offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times.
During laparoscopic cyst deroofing, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, and a small incision is made near the navel. Carbon dioxide gas is then introduced into the abdominal cavity to create space for the surgeon to work. Next, a laparoscope, which is a thin, flexible tube with a camera at its tip, is inserted through the incision, allowing the surgeon to visualize the cyst and surrounding tissue on a monitor.
Additional small incisions may be made to accommodate specialized surgical instruments. The surgeon carefully removes the cyst's roof, which is the outer layer or wall, while preserving healthy tissue. This process involves precise dissection and cauterization to minimize bleeding.
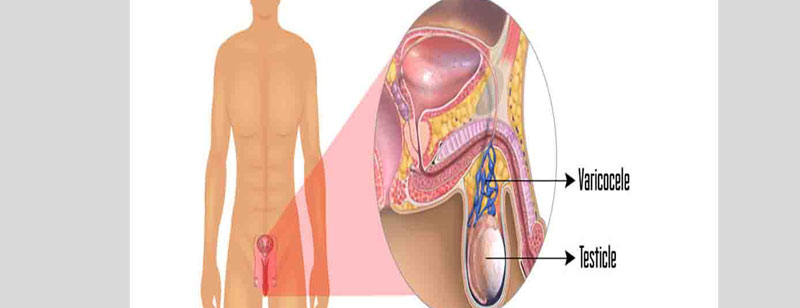
Microscopic varicolectomy is a highly specialized surgical procedure designed to treat varicoceles, which are dilated and swollen veins within the scrotum. These varicose veins can lead to male infertility, testicular pain, or discomfort, and microscopic varicolectomy aims to alleviate these issues.
During a microscopic varicolectomy, the patient is typically placed under general or local anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision, usually in the upper part of the scrotum, and then uses a high-powered surgical microscope to magnify the area. This advanced visualization allows for precise identification and preservation of vital structures like arteries and lymphatics while isolating and ligating the problematic veins.
Once the enlarged veins are identified, the surgeon carefully ties them off or seals them using tiny sutures or clips. This process redirects blood flow away from the varicocele, effectively reducing its size and pressure on the testicular arteries and veins. The minimally invasive approach ensures minimal scarring, a shorter recovery time, and a lower risk of complications compared to traditional open varicocelectomy.
Microscopic varicolectomy has shown high success rates in improving fertility and relieving pain associated with varicoceles. It is particularly beneficial for men seeking to address infertility issues, as it helps enhance sperm quality and motility by restoring healthier blood circulation in the testes. Patients often experience minimal discomfort, a quick recovery, and a significant improvement in their overall reproductive health.